
很多人都听说过爬虫,我也不例外。曾看到别人编写的爬虫代码,虽然没有深入研究,但感觉非常强大。因此,今天我决定从零开始,花费仅5分钟学习入门爬虫技术,以后只需轻轻一爬就能查看所有感兴趣的网站内容。广告?不存在的,因为我看不见。爬虫只会获取我感兴趣的信息,不需要的内容对我而言只是一堆代码。我们不在乎网站的界面,爬取完数据后只会关注最核心的内容。
在这个过程中,技术方面实际上没有太多复杂的内容,实际上就是一项耐心细致的工作。因此才会有那么多人选择从事爬虫兼职工作,因为虽然耗时较长,但技术要求并不是很高。今天学完之后,你就不会像我一样认为爬虫很困难了。或许在未来你会需要考虑如何保持会话(session)或者绕过验证等问题,因为网站越难爬取,说明对方并不希望被爬取。实际上,这部分内容是最具挑战性的,有机会的话我们可以在以后的学习中深入讨论。
今天我们以选择菜谱为案例,来解决我们在吃饭时所面临的“吃什么”的生活难题。
爬虫解析
爬虫的工作原理类似于模拟用户在浏览网站时的操作:首先访问官方网站,检查是否有需要点击的链接,若有,则继续点击查看。当直接发现所需的图片或文字时,即可进行下载或复制。这种爬虫的基本架构如图所示,希望这样的描述能帮助你更好地理解。
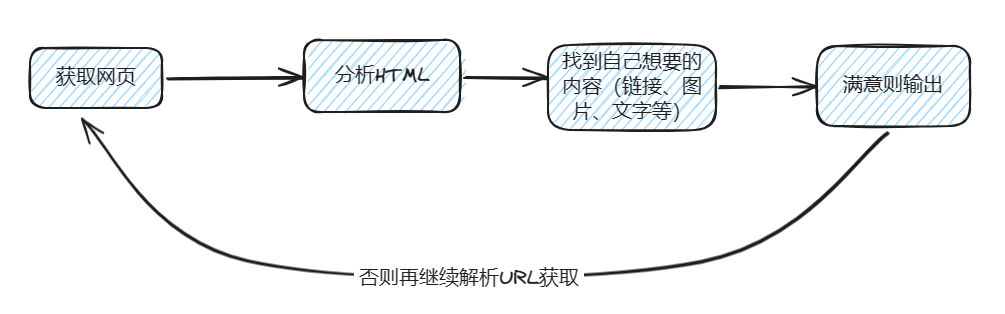
爬网页HTML
在进行爬虫工作时,我们通常从第一步开始,即发送一个HTTP请求以获取返回的数据。在我们的工作中,通常会请求一个链接以获取JSON格式的信息,以便进行业务处理。然而,爬虫的工作方式略有不同,因为我们需要首先获取网页内容,因此这一步通常返回的是HTML页面。在Python中,有许多请求库可供选择,我只举一个例子作为参考,但你可以根据实际需求选择其他第三方库,只要能够完成任务即可。
在开始爬虫工作之前,首先需要安装所需的第三方库依赖。这部分很简单,只需根据需要安装相应的库即可,没有太多复杂的步骤。
让我们不多废话,直接看下面的代码示例:
from urllib.request import urlopen,Request
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/122.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/122.0.0.0'}
req = Request("https://www.meishij.net/?from=space_block",headers=headers)
# 发出请求,获取html
# 获取的html内容是字节,将其转化为字符串
html = urlopen(req)
html_text = bytes.decode(html.read())
print(html_text)
通常情况下,我们可以获取这个菜谱网页的完整内容,就像我们在浏览器中按下F12查看的网页源代码一样。
解析元素
最笨的方法是使用字符串解析,但由于Python有许多第三方库可以解决这个问题,因此我们可以使用BeautifulSoup来解析HTML。其他更多的解析方法就不一一介绍了,我们需要用到什么就去搜索即可,不需要经常使用的也没必要死记硬背。
热搜菜谱
在这里,让我们对热门搜索中的菜谱进行解析和分析。
from urllib.request import urlopen,Request
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bf
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/122.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/122.0.0.0'}
req = Request("https://www.meishij.net/?from=space_block",headers=headers)
# 发出请求,获取html
# 获取的html内容是字节,将其转化为字符串
html = urlopen(req)
html_text = bytes.decode(html.read())
# print(html_text)
# 用BeautifulSoup解析html
obj = bf(html_text,'html.parser')
# print(html_text)
# 使用find_all函数获取所有图片的信息
index_hotlist = obj.find_all('a',class_='sancan_item')
# 分别打印每个图片的信息
for ul in index_hotlist:
for
li in ul.find_all('strong',class_='title'):
print(li.get_text())
主要步骤是,首先在上一步中打印出HTML页面,然后通过肉眼观察确定所需内容位于哪个元素下,接着利用BeautifulSoup定位该元素并提取出所需信息。在我的情况下,我提取的是文字内容,因此成功提取了所有li列表元素。
随机干饭
在生活中,实际上干饭并不复杂,难点在于选择吃什么。因此,我们可以将所有菜谱解析并存储在一个列表中,然后让程序随机选择菜谱。这样,就能更轻松地解决每顿饭吃什么的难题了。
随机选取一道菜时,可以使用以下示例代码:
from urllib.request import urlopen,Request
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bf
for i in range(3):
url = f"https://www.meishij.net/chufang/diy/jiangchangcaipu/?&page={i}"
html = urlopen(url)
# 获取的html内容是字节,将其转化为字符串
html_text = bytes.decode(html.read())
# print(html_text)
obj = bf(html_text,'html.parser')
index_hotlist = obj.find_all('img')
for p in index_hotlist:
if p.get('alt'):
print(p.get('alt'))
这里我们在这个网站上找到了新的链接地址,我已经获取了前三页的数据,并进行了随机选择,你可以选择全部获取。
菜谱教程
其实上一步已经完成了,接下来只需下单外卖了。外卖种类繁多,但对于像我这样的顾家奶爸来说并不合适,因此我必须自己动手做饭。这时候教程就显得尤为重要了。
我们现在继续深入解析教程内容:
from urllib.request import urlopen,Request
import urllib,string
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bf
url = f"https://so.meishij.net/index.php?q=红烧排骨"
url = urllib.parse.quote(url, safe=string.printable)
html = urlopen(url)
# 获取的html内容是字节,将其转化为字符串
html_text = bytes.decode(html.read())
obj = bf(html_text,'html.parser')
index_hotlist = obj.find_all('a',class_='img')
# 分别打印每个图片的信息
url = index_hotlist[0].get('href')
html = urlopen(url)
html_text = bytes.decode(html.read())
obj = bf(html_text,'html.parser')
index_hotlist = obj.find_all('div',class_='step_content')
for div in index_hotlist:
for p in div.find_all('p'):
print(p.get_text())
包装一下
上面提到的方法已经满足了我们的需求,但是重复手动执行每个步骤并不是一个高效的方式。因此,我将这些步骤封装成一个简单的应用程序。这个应用程序使用控制台作为用户界面,不需要依赖任何第三方库。让我们一起来看一下这个应用程序吧:
# 导入urllib库的urlopen函数
from urllib.request import urlopen,Request
import urllib,string
# 导入BeautifulSoup
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bf
from random import choice,sample
from colorama import init
from os import system
from
termcolor import colored
from readchar import readkey
FGS = ['green', 'yellow', 'blue', 'cyan', 'magenta', 'red']
print(colored('搜索食谱中.....',choice(FGS)))
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/122.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/122.0.0.0'}
req = Request("https://www.meishij.net/?from=space_block",headers=headers)
# 发出请求,获取html
# 获取的html内容是字节,将其转化为字符串
html = urlopen(req)
html_text = bytes.decode(html.read())
hot_list = []
all_food = []
food_page = 3
# '\n'.join(pos(y, OFFSET[1]) + ' '.join(color(i) for i in l)
def draw_menu(menu_list):
clear()
for idx,i in enumerate(menu_list):
print(colored(f'{idx}:{i}',choice(FGS)))
print(colored('8:随机选择',choice(FGS)))
def draw_word(word_list):
clear()
for i in word_list:
print(colored(i,choice(FGS)))
def clear():
system("CLS")
def hot_list_func() :
global html_text
# 用BeautifulSoup解析html
obj = bf(html_text,'html.parser')
# print(html_text)
# 使用find_all函数获取所有图片的信息
index_hotlist = obj.find_all('a',class_='sancan_item')
# 分别打印每个图片的信息
for ul in index_hotlist:
for li in ul.find_all('strong',class_='title'):
hot_list.append(li.get_text())
# print(li.get_text())
def search_food_detail(food) :
print('正在搜索详细教程,请稍等30秒左右!')
url = f"https://so.meishij.net/index.php?q={food}"
# print(url)
url = urllib.parse.quote(url, safe=string.printable)
html = urlopen(url)
# 获取的html内容是字节,将其转化为字符串
html_text = bytes.decode(html.read())
obj = bf(html_text,'html.parser')
index_hotlist = obj.find_all('a',class_='img')
# 分别打印每个图片的信息
url = index_hotlist[0].get('href')
# print(url)
html = urlopen(url)
html_text = bytes.decode(html.read())
# print(html_text)
obj = bf(html_text,'html.parser')
random_color = choice(FGS)
print(colored(f"{food}做法:",random_color))
index_hotlist = obj.find_all('div',class_='step_content')
# print(index_hotlist)
random_color = choice(FGS)
for div in index_hotlist:
for p in div.find_all('p'):
print(colored(p.get_text(),random_color))
def get_random_food():
global food_page
if not all_food :
for i in range(food_page):
url = f"https://www.meishij.net/chufang/diy/jiangchangcaipu/?&page={i}"
html = urlopen(url)
# 获取的html内容是字节,将其转化为字符串
html_text = bytes.decode(html.read())
# print(html_text)
obj = bf(html_text,'html.parser')
index_hotlist = obj.find_all('img')
for p in index_hotlist:
if p.get('alt'):
all_food.append(p.get('alt'))
my_food = choice(all_food)
print(colored(f'随机选择,今天吃:{my_food}',choice(FGS)))
return my_food
init() ## 命令行输出彩色文字
hot_list_func()
print(colored('已搜索完毕!',choice(FGS)))
my_array = list(range(0, 9))
my_key = ['q','c','d','m']
my_key.extend(my_array)
print(colored('m:代表今日菜谱',choice(FGS)))
print(colored('c:代表清空控制台',choice(FGS)))
print(colored('d:代表菜谱教程',choice(FGS)))
print(colored('q:退出菜谱',choice(FGS)))
print(colored('0~8:选择菜谱中的菜',choice(FGS)))
while True:
while True:
move = readkey()
if move in my_key or (move.isdigit() and int(move) <= len(random_food)):
break
if move == 'q': ## 键盘‘Q’是退出
break
if move == 'c': ## 键盘‘C’是清空控制台
clear()
if move == 'm':
random_food = sample(hot_list,8)
draw_menu(random_food)
if move.isdigit() and int(move) <= len(random_food):
if int(move) == 8:
my_food = get_random_food()
else:
my_food = random_food[int(move)]
print(my_food)
if move == 'd' and my_food : ## 键盘‘D’是查看教程
search_food_detail(my_food)
my_food = ''
完成一个简单的小爬虫其实并不复杂,如果不考虑额外的封装步骤,仅需5分钟即可完成,这已经足够快速让你入门爬虫技术。开始爬取某个网站的数据实际上是一项细致的工作。只需在网上搜索相关技术信息,找到适合的方法即可,如果有效就继续使用,不行就试试其他方法。
总结
本文的重点在于引导读者如何初步掌握爬虫技术。初步掌握爬虫技术并不难,但是在实际操作中可能会遇到一些困难,比如一些网站不允许直接访问,需要登录或者进行各种人机验证等。因此,最好先从爬取一些新闻资讯类的网站开始,因为这样相对容易。涉及用户支付等敏感信息的网站就不那么容易获取了。因此,在入门阶段,建议不要纠结于选择一个复杂的网站,先尝试入门即可。一旦理解了基本原理,遇到问题时就可以考虑添加组件或者使用第三方库来解决。
最终,我真诚地希望本文对你有所帮助。如果你觉得内容有趣或有用,不妨动动小手,点个关注支持一下,嘻嘻。
链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/guoxiaoyu/p/18063239
(版权归原作者所有,侵删)